
What is the Difference Between Average Speed and Average Velocity?
Average Speed And Average Velocity are fundamental concepts in physics that describe how fast objects move. While these terms are often confused, average speed measures the total distance traveled per unit time regardless of direction, whereas average velocity considers displacement and direction. Understanding the average speed and average velocity difference is crucial for analyzing motion in physics, particularly for students in classes 9 and 11.
Fundamental Concepts: Distance vs Displacement
Before exploring average speed and average velocity definitions, we must distinguish between distance and displacement. Distance is a scalar quantity representing the total path length traveled by an object. Displacement, however, is a vector quantity that measures the shortest straight-line distance between initial and final positions, including direction.
Consider a runner completing one lap around a circular track. The distance traveled equals the track's circumference, while the displacement is zero since the runner returns to the starting point. This distinction is fundamental to understanding the difference between distance and displacement in motion analysis.
Speed and Velocity: Basic Definitions
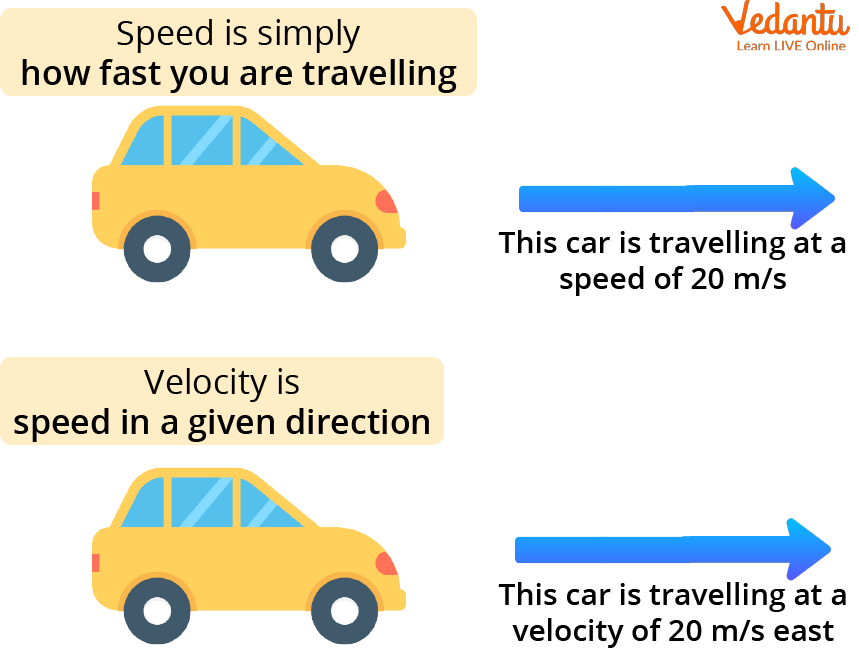
Speed is a scalar quantity that indicates how fast an object moves without considering direction. It represents the rate of change of distance with respect to time.
Velocity is a vector quantity that describes the rate of change of displacement with respect to time. Unlike speed, velocity includes directional information.
Speed is measured in units like meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h), while velocity uses the same units but includes directional components.
Average Speed and Average Velocity Formula
The average speed and average velocity formula provides the mathematical foundation for analyzing motion over specific time intervals.
Average Speed Formula
Average Speed Formula: The average speed is calculated by dividing the total distance traveled by the total time taken.
Where $v_{avg}$ is average speed, $d_{total}$ is total distance, and $t_{total}$ is total time.
Average Velocity Formula
Average Velocity Formula: Average velocity equals the total displacement divided by the total time.
Where $\vec{v}_{avg}$ is average velocity (vector), $\vec{s}$ is displacement (vector), and $t_{total}$ is total time.
Difference Between Average Speed and Average Velocity
Understanding the difference between average speed and average velocity with examples helps clarify these concepts for practical applications.
| Aspect | Average Speed | Average Velocity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total distance divided by total time | Total displacement divided by total time |
| Quantity Type | Scalar (magnitude only) | Vector (magnitude and direction) |
| Direction Consideration | No directional information | Includes directional information |
| Value for Round Trip | Always positive | Zero if returning to start |
| SI Units | m/s, km/h | m/s, km/h (with direction) |
Average Speed and Average Velocity Numericals Class 9
Let's solve some practical problems to understand these concepts better.
Example 1: Simple Motion
A car travels 200 km in 4 hours. Calculate the average speed.
Solution:
- Given: Distance = 200 km, Time = 4 hours
- Apply formula: $v_{avg} = \frac{d_{total}}{t_{total}}$
- Calculate: $v_{avg} = \frac{200 \text{ km}}{4 \text{ hours}} = 50 \text{ km/h}$
Example 2: Motion with Direction Change
A person walks 30 meters east, then 40 meters west in 10 seconds total. Find average speed and average velocity.
Solution:
FAQs on Average Speed and Average Velocity: Complete Guide with Formula and Examples
1. What is the difference between average speed and average velocity?
Average speed is the total distance travelled divided by the total time taken, while average velocity is the total displacement divided by total time. Key differences include:
- Average speed is a scalar quantity (only magnitude, no direction).
- Average velocity is a vector quantity (magnitude and direction).
- If an object returns to its starting point, average velocity can be zero, but average speed cannot.
2. How do you calculate average speed?
To find average speed, divide the total distance travelled by the total time taken:
- Average speed = Total distance / Total time
- Always a positive value
- Measured in meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h)
3. How do you find average velocity?
Average velocity is calculated by dividing the total displacement by total time taken:
- Average velocity = Total displacement / Total time
- It has both magnitude and direction
- Can be zero if the object returns to the starting point
4. Can average speed and average velocity be equal?
Yes, average speed and average velocity can be equal if the total distance travelled equals the magnitude of total displacement. This usually happens when the motion is along a straight line in one direction.
5. Why is average velocity sometimes zero while average speed is not?
Average velocity can be zero if the total displacement is zero, even though the total distance travelled is not zero. For example:
- If an object returns to its starting point, displacement is zero, so average velocity is zero.
- Average speed, which depends on distance, will still be positive.
6. What is displacement and how does it relate to average velocity?
Displacement is the shortest straight-line distance from the initial to the final position of an object, and it has direction.
- Average velocity = Displacement / Time
- Displacement determines both the magnitude and direction of average velocity.
7. In what units are average speed and average velocity measured?
Both average speed and average velocity are measured in the same units, most commonly:
- meters per second (m/s)
- kilometers per hour (km/h)
- The choice of unit depends on the context or problem given.
8. Define average speed and give its formula.
Average speed is the total distance covered divided by the total time taken. Its formula is:
- Average speed = Total distance / Total time
- It is a scalar quantity and always positive.
9. State one example each where average speed and average velocity are different.
When an object moves along a circular track and returns to its starting point:
- Average speed is the total distance completed divided by total time (full length of the path).
- Average velocity is zero because displacement is zero.
10. What happens to average speed and average velocity if a car returns to its starting point?
If a car returns to its starting point, average velocity becomes zero (as displacement is zero), but average speed remains positive (as the total distance covered is not zero).
11. Does the path taken affect average speed and average velocity? How?
Yes, average speed depends on the total path (distance) taken, while average velocity depends only on displacement (shortest distance between start and finish).
- If the path is curved or not straight, average speed will usually be greater than the magnitude of average velocity.
12. What is the SI unit of average velocity?
The SI unit of average velocity is meter per second (m/s).